コレクション talipes club foot types 297221
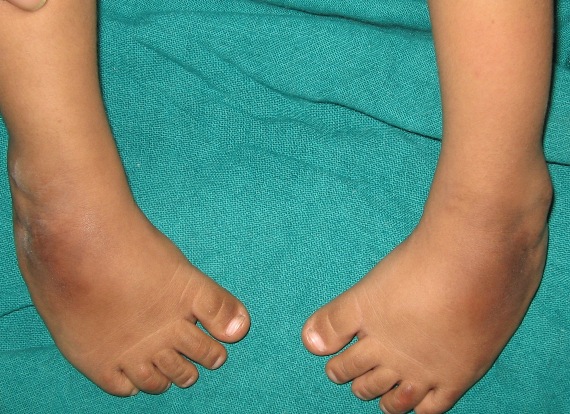
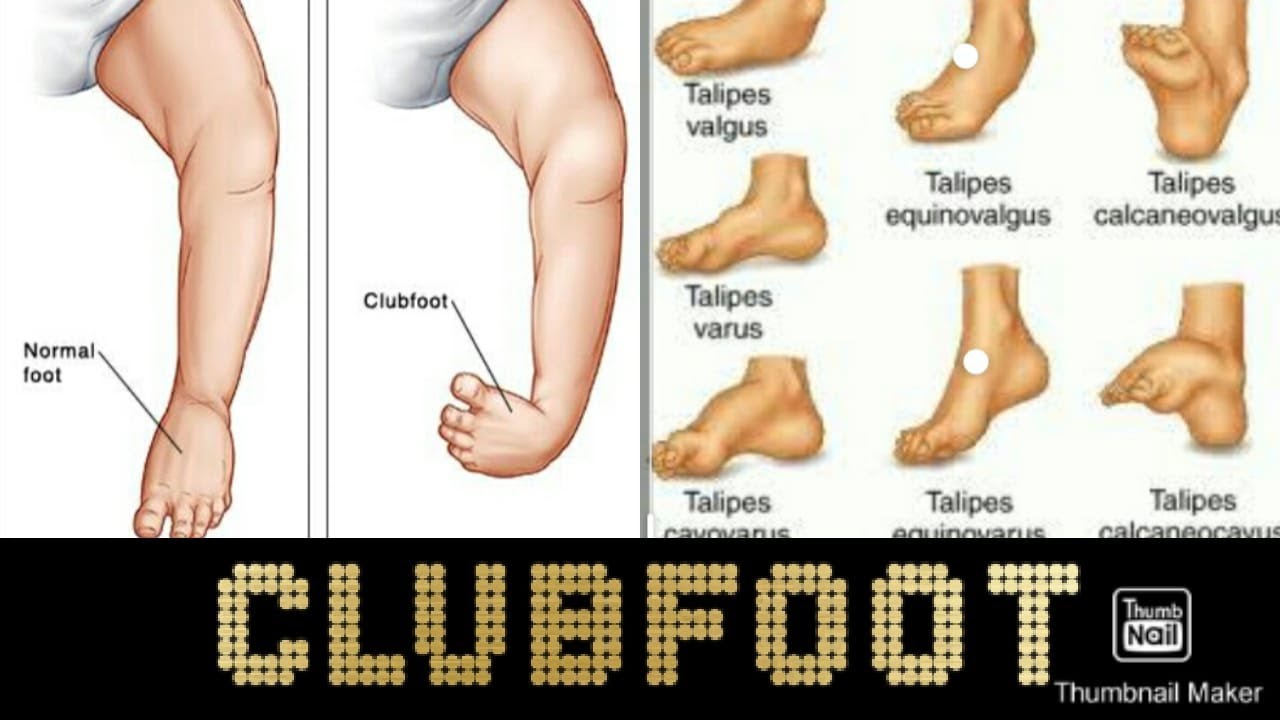
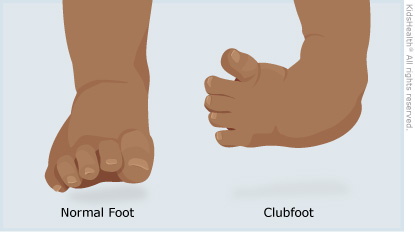
Diagnosis Most commonly, a doctor recognizes clubfoot soon after birth just from looking at the shape and positioning of the newborn's foot Occasionally, the doctor may request Xrays to fully understand how severe the clubfoot is, but usually Xrays are not necessary Talipes equinovarus, commonly known as "clubfoot," is a congenital deformity of the foot It is characterized by plantar flexion (equinus), inversion (varus), and an exaggerated arch (cavus) that may involve one or both feet Taken together, these deformities are said make the foot resemble a golf club, hence the nameClubfoot Clubfoot is a deformity in which an infant's foot is turned inward, often so severely that the bottom of the foot faces sideways or even upward Approximately one infant in every 1,000 live births will have clubfoot, making it one of the more common congenital (present at

Challenging Clubfeet The Arthrogrypotic Clubfoot And The Complex Clubfoot Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics
Talipes club foot types
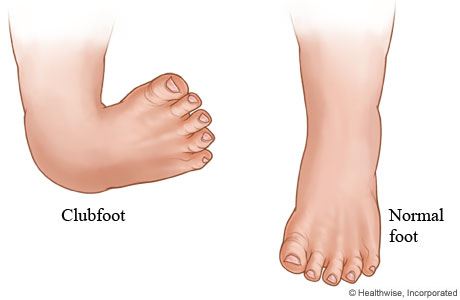
Talipes club foot types- What are the different types of talipes?Clubfoot doesn't cause pain, but if it's not treated, it can make it hard for a child to walk without a limp It's easy to correct in most cases, so most children don't have longlasting



Understanding Talipes Club Foot Torc2 Ltd
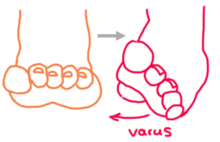
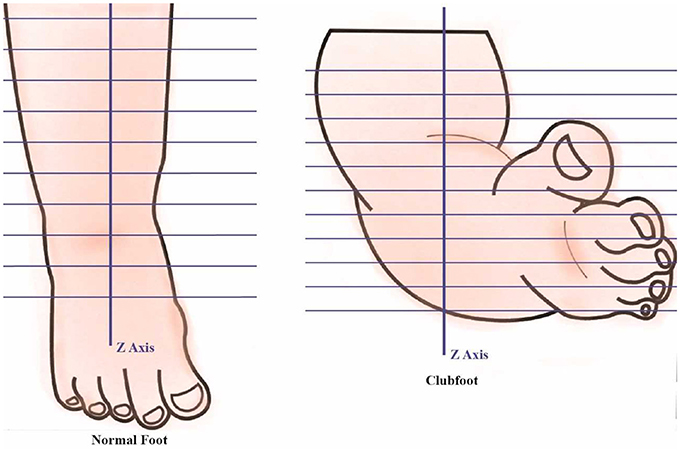
Talipes equinovarus, sometimes called clubfoot, is characterized by plantar flexion, inward tilting of the heel (from the midline of the leg), and adduction of the forefoot (medial deviation away from the leg's vertical axis)Clubfoot, or talipes equinovarus, is a deformity in which the foot is excessively plantar flexed, with the forefoot bent medially and the sole facing inwardThis usually results in the underdevelopment of the soft tissues on the medial side of the foot and Talipes equinovarus (TEV) is a specific and common type of what is sometimes called "clubfoot", a term that encompasses a range of anomalies of the ankle or foot present at birth (see Fig 433)TEV can be defined as fixation of the foot (forefoot and hindfoot) in plantar flexion (equinus), deviation toward the midline (varus) and upward rotation so the foot rests on
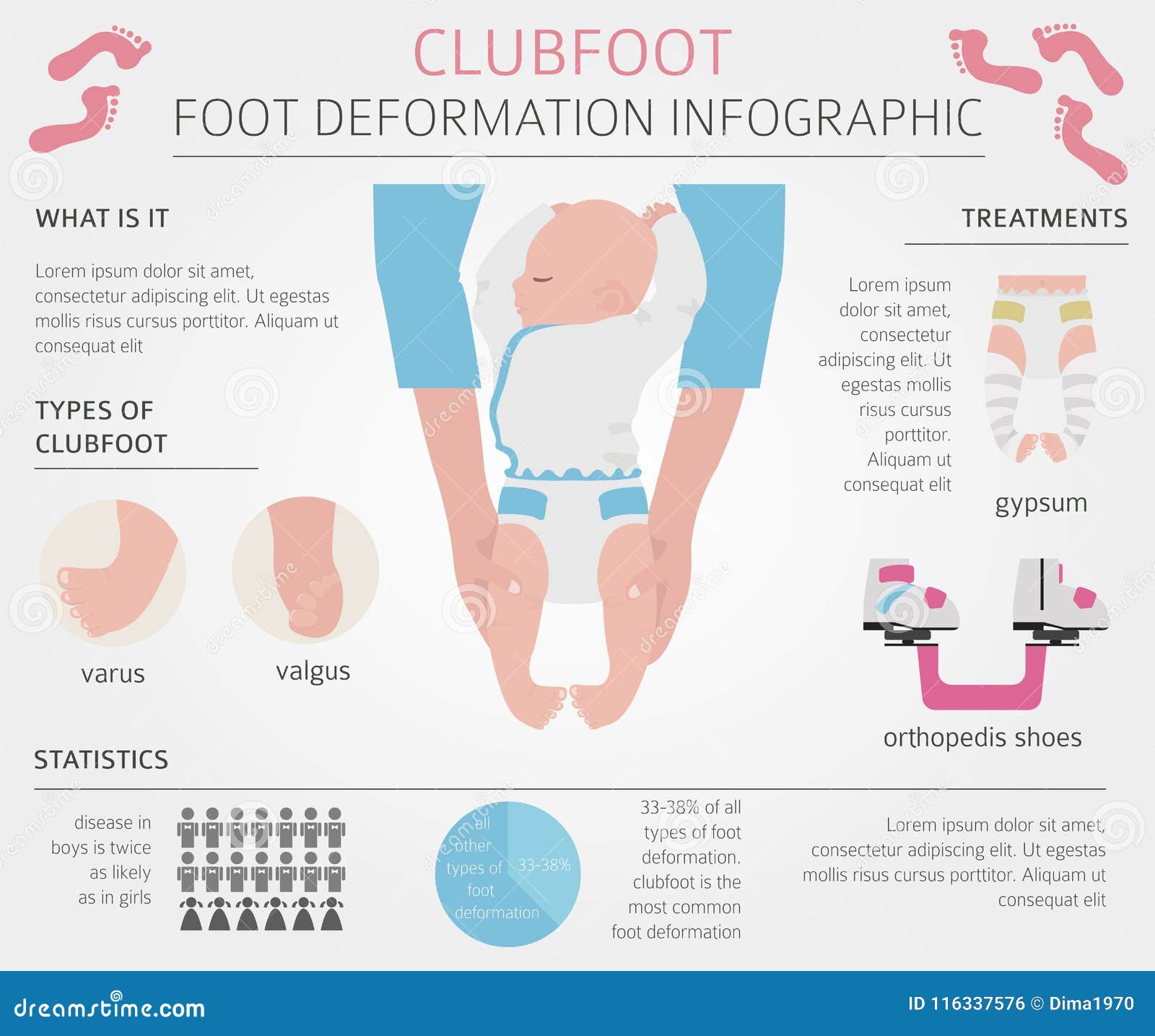
Talipes covers several physical foot conditions that a baby may be born with One type of talipes is commonly known as club foot Find out the difference between the types of talipes, and how each condition is treatedComplex Clubfoot any foot with deformity that has received any type of treatment other than the Ponseti method may have added complexity because of additional pathology or scarring from surgery Resistant Clubfoot this is a clubfoot where Ponseti treatment has been correctly performed but there has been no significant improvement It is often found that this type of clubfoot Club Foot also is known as Giles Smith Syndrome, Congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV), or talipes equinovarus (TEV) The Word "Talipes Equinovarus" comes from Latin Talus (ankle) pes (foot)Equino– indicates the heel is elevated (like a horse's) varusindicates it is turned inward The foot is turned in sharply, and the person seems to be walking on their ankle
Clubfoot or talipes equinovarus (TEV) is an inborn threedimensional deformity of leg, ankle and foot It results from structural defects of several tissues of foot and lower leg leading to abnormal positioning of foot and ankle joints TEV can lead to longlasting functional disability, malformatioClubfoot (talipes equinovarus) Clubfoot is a common foot deformity in newborns, affecting about 1 in 1,000 babies It may be mild or severe, and may affect one or both feet In clubfoot, the bones, joints, ligaments and muscles of the foot are abnormal The foot turns down and inwards (Figure 1) If only one foot is affected, that foot and calfThere are two types of clubfoot Isolated or idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type If your child has clubfoot with no other medical problems, it's called isolated clubfoot Idiopathic means that the cause of clubfoot is not known Nonisolated clubfoot



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments




Clubfoot
Condition from birth deformity of the feet bilateral talipes equinovarus See more ideas about club foot, club foot baby, feetEach type of clubfoot has unique characteristics and may need specific treatment Early recognition of the type of clubfoot one is dealing with can help guide appropriate treatment Individuals with clubfoot experience bone and soft tissues deformation and this abnormality can be presented through a range of abnormal alignmentsTypes of Clubfoot There are three types of clubfoot that your child can be diagnosed with Idiopathic Clubfoot A true (idiopathic) clubfoot accounts for the vast majority of cases This type is stiff or rigid, and very hard to manipulate Positional Clubfoot



Clubfoot Global Indian Nurses Organization




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets
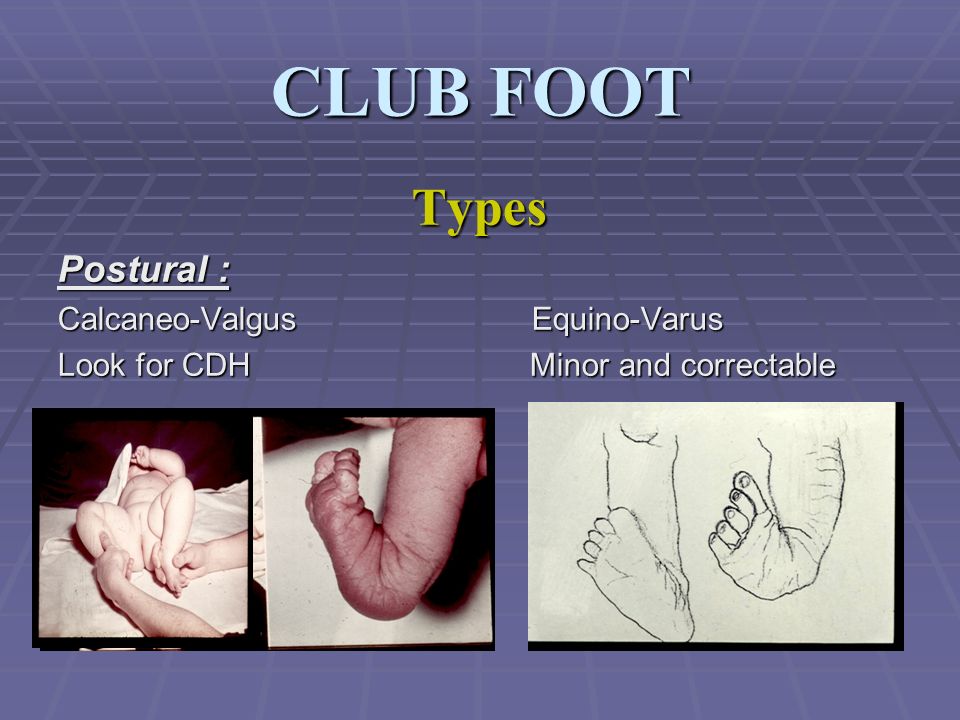
Positional talipes usually improves with gentle stretches There are 2 main types of positional talipes, depending on the position of your baby's feet 1 Talipes Equinovarus Where your baby's foot turns inwards and the front half of the foot points down 2 Talipes Calcaneovalgus Where your baby's foot is pushed up and the front halfClub foot (also called talipes) is where a baby is born with a foot or feet that turn in and under Early treatment should correct it In club foot, 1 foot or both feet point down and inwards with the sole of the foot facing backwards Credit Club foot happens because the Achilles tendon (the large tendon at the back of the ankle) is too shortSyndromic clubfoot occurs due to some other clinical conditions Arthrogryposis, tibial hemimelia, constriction band syndrome, and diastrophic dwarfism are examples of syndromes that cause clubfoot



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os



1
Clubfoot (congenital talipes equinovarus) Clubfoot, also known as congenital talipes equinovarus, is a common idiopathic deformity of the foot that presents in neonates Diagnosis is made clinically with a resting equinovarus deformity of the foot Treatment is usually ponseti method castingClubfoot is a foot deformity classified into three different types idiopathic (unknown cause), neurogenic (caused by condition of the nervous system) and syndromic (related to an underlying syndrome) Idiopathic Clubfoot Also known as talipes equinovarus, idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type of clubfoot and is present at birthTalipes equinovarus Incidence Clubfoot is a common defect present at birth and occurs in every 1,000 live births Bilateral TEV can be found be found in nearly 50% of cases About twice as many males are born with the congenital form than females Talipes equinovarus Types




Pdf Reverse Club Foot Rigid And Recalcitrant Talipes Calcaneovalgus Semantic Scholar



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine
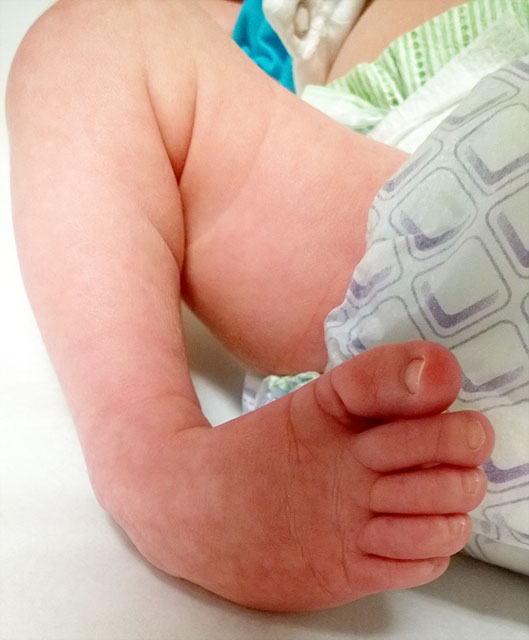
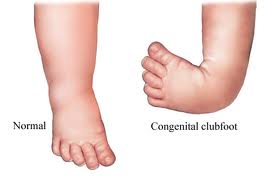
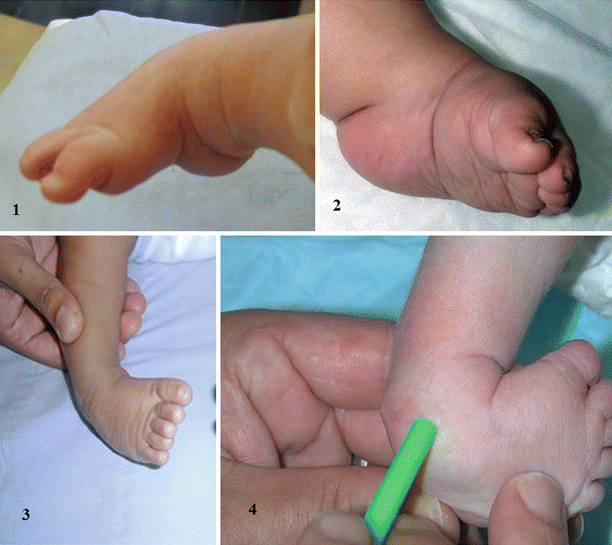
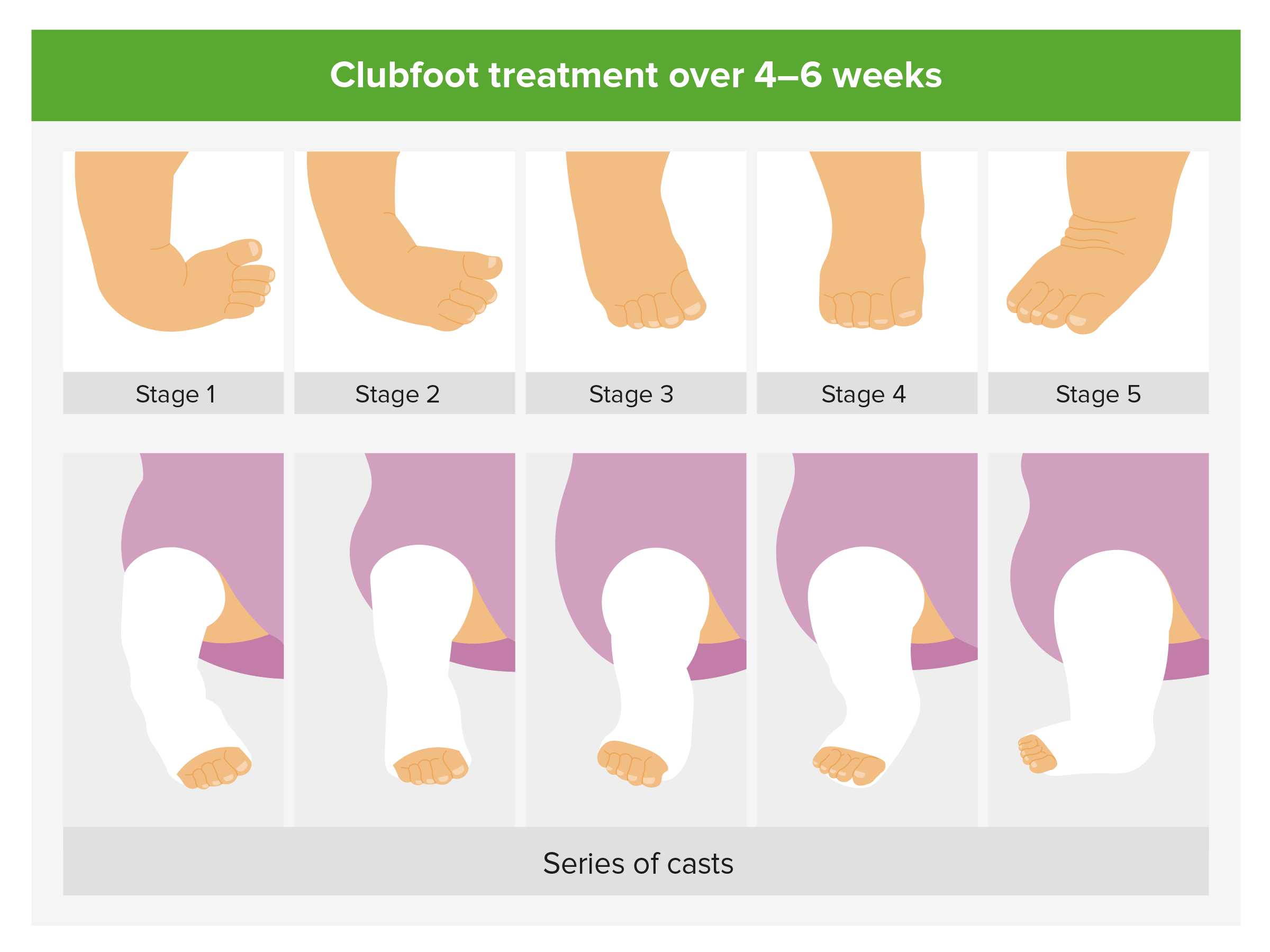
Clubfoot, also known as talipes equinovarus, is a condition where a baby's foot is twisted inward to the point where the bottom of the foot faces sideways and in some cases upward When a child has clubfoot, their feet and legs have all the same bones, tendons and muscles as a healthy child, but they are positioned incorrectlyTreatment of Talipes / Clubfoot The late Dr Ignacio Ponseti from Iowa, developed the Ponseti method, a minimally invasive treatment for clubfoot The Ponseti Method involves weekly sessions in which a specialist manipulates your baby's foot with their hands, gradually correcting the position of the foot A plaster cast is then applied from Clubfoot describes a range of foot abnormalities usually present at birth (congenital) in which your baby's foot is twisted out of shape or position In clubfoot, the tissues connecting the muscles to the bone (tendons) are shorter than usual Clubfoot is a fairly common birth defect and is usually an isolated problem for an otherwise healthy



Congenital Clubfoot Early Recognition And Conservative Management For Preventing Late Disabilities Springerlink



What A Paediatrician Should Know About Congenital Clubfoot Italian Journal Of Pediatrics Full Text
Clubfoot (talipes) occurs when a baby is born with a foot and ankle twisted out of shape or position One of the more wellknown forms of talipes is clubfoot (talipes equinovarus) However, there are other forms of the condition Talipes is a common condition and its diagnosis can be very worrying for parents Talipes equinovarus (TEV) is the specific term and common type of what is sometimes called "clubfoot", a term that encompasses a range of anomalies of the ankle or foot present at birth Fig 34 Talipes equinovarus CLUB FOOT Types Idiopathic (Unknown Etiology) CongenitalTalipes EquinoVarus CTEV Acquired, Secondary to CNS Disease Spina bifida, Poliomyelitis Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita Absent Bone fibula / tibia 10 CTEV MOST COMMON CONGENITAL FOOT DISORDER MALES 1/1000 LIVES BIRTHS 11




Talipes Club Foot Health



Clubfoot Wikipedia
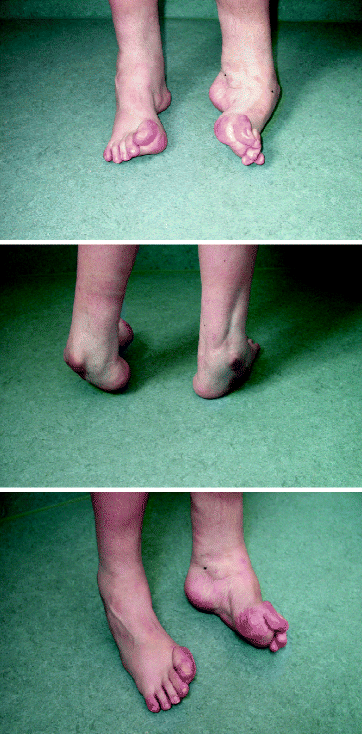
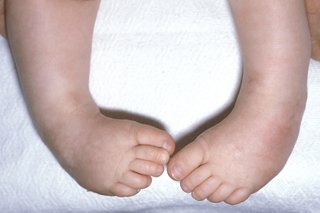
Family studies and the course of congenital clubfoot, talipes equinovarus, talipes calcaneovalgus, and metatarsus varus Dr Wheeless enjoys and performs all types of orthopaedic surgery but is renowned for his expertise in total joint arthroplasty (Hip and Knee replacement) as well as complex joint infectionsClubfoot is a birth defect where one or both feet are rotated inward and downward The affected foot and leg may be smaller than the other Approximately 50% of cases of clubfoot affect both feet Most of the time, it is not associated with other problems Without treatment, the foot remains deformed, and people walk on the sides of their feet This may lead to pain and difficulty walking Picture 1 – Talipes equinovarus Club foot;




Challenging Clubfeet The Arthrogrypotic Clubfoot And The Complex Clubfoot Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics




Club Foot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus About Club Foot Patient
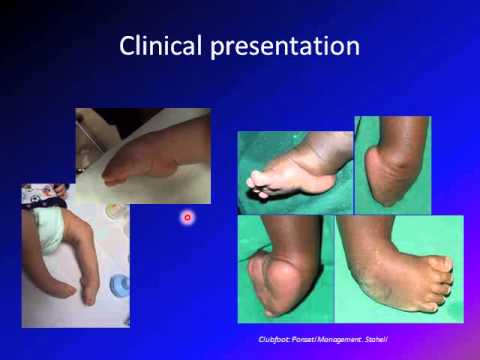
This video explain the etiology, clinical presentation, incidence, types and management of clubfoot It provides excellent overview for this condition and heWhile some use talipes equinovarus and clubfoot synonymously, in certain publications, the term clubfoot is considered a more general descriptive term that describes three distinct abnormalities talipes equinovarus (adduction of the forefoot, inversion of the heel and plantar flexion of the forefoot and ankle)N Clubfoot (Talipes Equinovarus) n Clubfoot is a relatively common foot deformity Sometimes it affects the entire lower leg as well as the foot In the most common type, clubfoot is the only birth defect present Treatment starts with a series of casts If this doesn't correct your



Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Or Club Foot Bone And Spine




Foot Deformities Various Talipes Conditions Pediatric Physical Therapy Pediatric Nursing Medical Terms
Clubfoot Clubfoot, also known as talipes equinovarus, is a congenital (present at birth) foot deformity in which the foot is curved toward the middle of the body, and the toes point downward It affects the bones, muscles, tendons and blood vessels (of the limb) and can affect one or both feet The foot is usually short and broad in appearanceBackground Congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV), which is also known as clubfoot, is a common congenital orthopaedic condition It is characterised by an excessively turned in foot (equinovarus) and high medial longitudinal arch (cavus) If left untreated it can result in longterm disability, deformity and painClubfoot, also known as talipes equinovarus (TEV), is a common foot abnormality, in which the foot points downward and inward The condition is present at birth, and involves the foot and lower leg It occurs twice as often (21) in males than in females It may affect one or




Clubfoot Phenotype In Pma Pma Mice Human Newborn With Congenital Download Scientific Diagram




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets
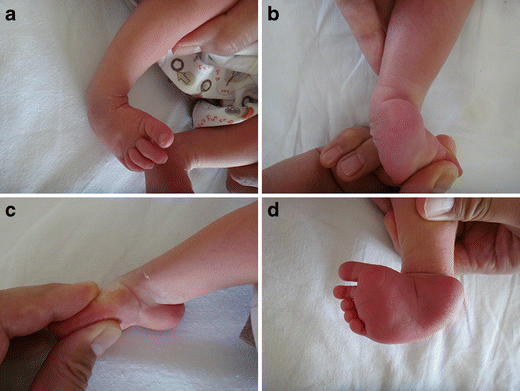
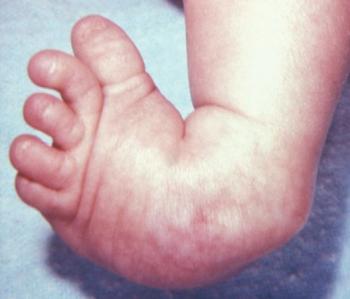
The clubfoot deformity is often referred to as congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV) Congenital clubfoot is a rigid deformity present at birth characterized by ankle equinus, heel tilt into varus, and midfoot and forefoot adduction with varus tiltAnd downwards (talipes equinovarus) Much more rarely the foot is turned downwards and outwards (talipes equinovalgus) In the past, talipes was called clubfoot There are two types of talipes and it is important to know and understand which one your baby has Positional Talipes Where the baby's foot is turned, but it is flexible,Club foot also known to doctors as congenital talipes equinovarus, is a common birth defect (congenital clubfoot) that can affect one or both feet The child is born with a foot pointing the wrong way – turned down and in – that cannot be placed flat on the ground in the position needed for walking (Figure 1)




Talipes High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Challenging Clubfeet The Arthrogrypotic Clubfoot And The Complex Clubfoot Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics
The most common type of clubfoot is idiopathic, which means the cause is unknown Idiopathic clubfoot is not related to any other medical problems Feet of babies with this type of clubfoot are stiff and hard to manipulateCongenital talipes equinovarus, or club foot, is one of the commonest congenital orthopaedic conditions Its incidence in the UK is approximately live births and up to 50% of cases are Although it is sometimes recommended that idiopathic clubfoot (talipes) be treated as soon as possible, this condition does not constitute an orthopedic emergency 35 Traditionally, surgery for clubfoot has been indicated when a plateau has been reached in nonoperative treatment




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Archives African Journal Of Current Medical Research



Frontiers Developing A Three Dimensional 3d Assessment Method For Clubfoot A Study Protocol Physiology
Talipes is also known as club foot It is a deformity of the foot and ankle that a baby can be born with In about half of babies born with talipes, both feet are affected 'Talipes' means the ankle and foot; Practice Essentials Clubfoot (talipes) can be classified as either of the following Fixed or rigid These are either flexible (ie, correctable without surgery) or resistant (ie, requiring surgical release, though this is not entirely true according to the Ponseti experience 1, 2, 3 ) The Pirani, Goldner, Diméglio, Hospital for JointClubfoot can be classified as congenital, syndromic, or positional The congenital foot deformity affects the bones, muscles, tendons, and blood vessels of one or both feet Syndromic cases are associated with additional anatomic malformations and/or chromosomal or genetic abnormalities




Clubfoot Treatment Bilateral Club Feet Foot Pain



Club Foot Talipes Equinovarus Ankle Foot And Orthotic Centre
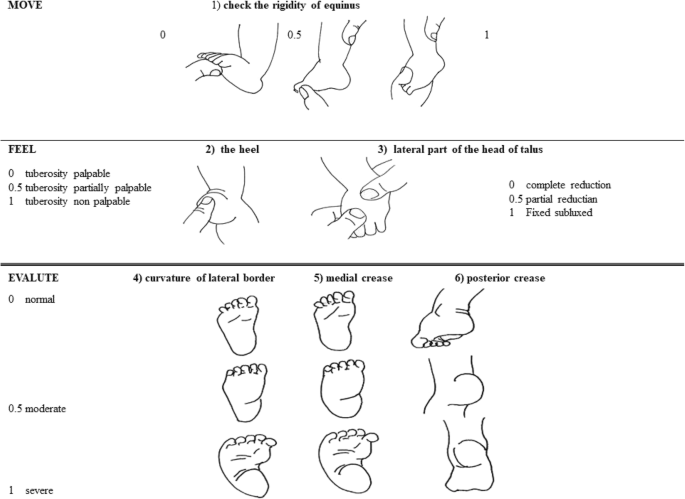
Clubfoot is a foot deformity classified into three different types idiopathic (unknown cause), neurogenic (caused by condition of the nervous system) and syndromic (related to an underlying syndrome)Congenital clubfoot is differentiated by structural, postural and secondary type The postural clubfoot can occur by abnormal position during birth and manipulative control The patient should be thoroughly examined to assess the features of paralytic clubfoot Congenital clubfoot can be rectifying completely Diagnostic tests Table 1 PiraniNeurogenic clubfoot may also develop later in children as a result of spinal cord compression or cerebral palsy Syndromic talipes;




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot Nursing Care Management Nurseslabs



The Current State Of Treatment For Clubfoot In Europe Springerlink
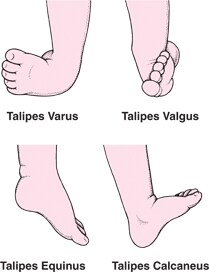
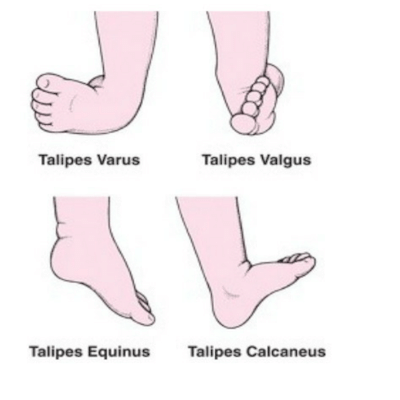
'equinovarus' refers to the position that the foot is in (see below) Talipes is a congenital condition These can increase the risk of clubfoot as well 13 TYPES Talipus varus inversion or bending inward of foot Talipes valgus eversion or bending outward of foot Talipes equinus planter flexion and toe is lowe than heel • Talipes calcaneous dorsiflexion, toe is higher than heelClubfoot, congenital twisting of the footIn the most common type, called talipes equinovarus, the heel bends upward and the front part of the foot is turned inward and bent toward the heelThe frequency of the disorder is equal in males and females A mild form, possibly caused by poor position in the womb, may be cured by the use of wrappings, plaster casts, and sometimes a




Orthokids Clubfoot




Clubfoot Repair Treatments Procedure Outlook




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets



Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Medicine Com



Understanding Talipes Club Foot Torc2 Ltd



Clubfoot Stock Illustrations 96 Clubfoot Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Clubfoot Flip Ebook Pages 1 Anyflip Anyflip



Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Congenital Clubfoot Ppt Video Online Download




Scielo Brasil Pe Torto Congenito Pe Torto Congenito




What Is Clubfoot Stanford Children S Health




Challenging Clubfeet The Arthrogrypotic Clubfoot And The Complex Clubfoot Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics




Clubfoot Wikipedia




Pdf Current Conservative Management And Classification Of Club Foot A Review Semantic Scholar



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia
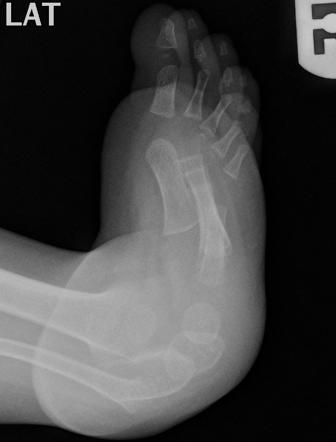



Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets




Club Foot Pdf Foot Congenital Disorder
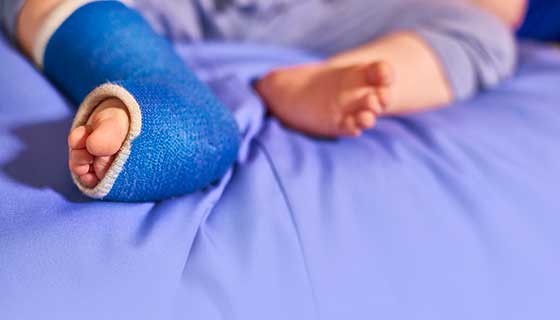



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine




Clubfoot Phenotype In Pma Pma Mice Human Newborn With Congenital Download Scientific Diagram




Clubfoot Nurse Key



Clubfoot Symptoms Stages Definition Description Demographics Causes And Symptoms Diagnosis




Club Foot Talipes In Babies Causes Signs Treatment Youtube




Clubfoot Healthing Ca




Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot And Other Foot Abnormalities Pediatrics Merck Manuals Professional Edition



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os




Treatment Of Relapsed Residual And Neglected Clubfoot Adjunctive Surgery Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics



Before Going To Doctor Which Must Know About Clubfoot Rxharun




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets
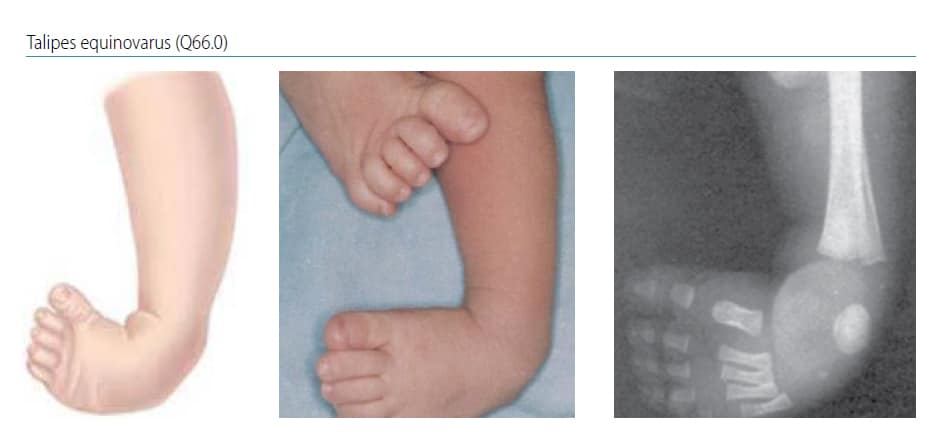



Chapter 4 9 Talipes Equinovarus Talipes Equinovarus Q66 0 Cdc
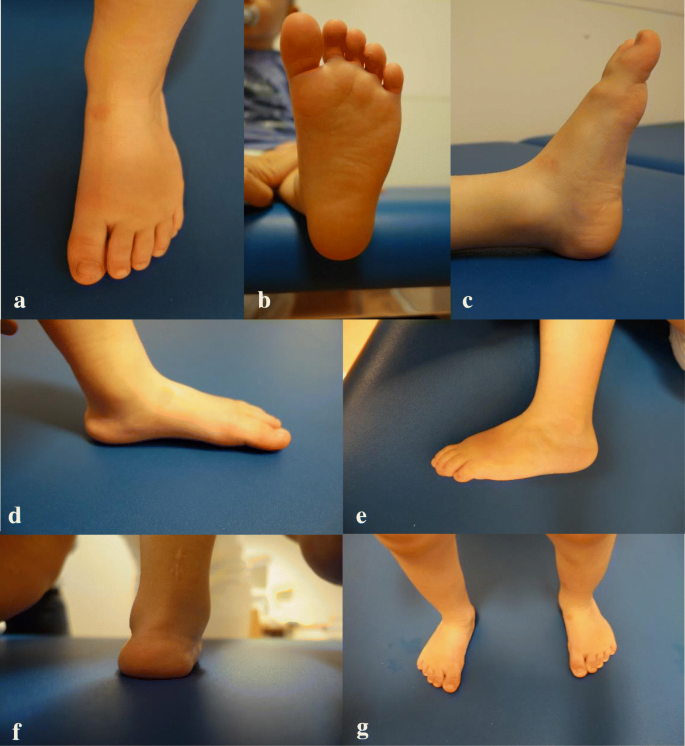



Is Unilateral Lower Leg Orthosis With A Circular Foot Unit In The Treatment Of Idiopathic Clubfeet A Reasonable Bracing Alternative In The Ponseti Method Five Year Results Of A Supraregional Paediatric Orthopaedic Centre



Clubfoot Its Types And Causes Simplified In Hindi Youtube



Evidence Based Treatment For Clubfoot Springerlink



Foot Deformities Concise Medical Knowledge



Clubfoot For Parents Nemours Kidshealth
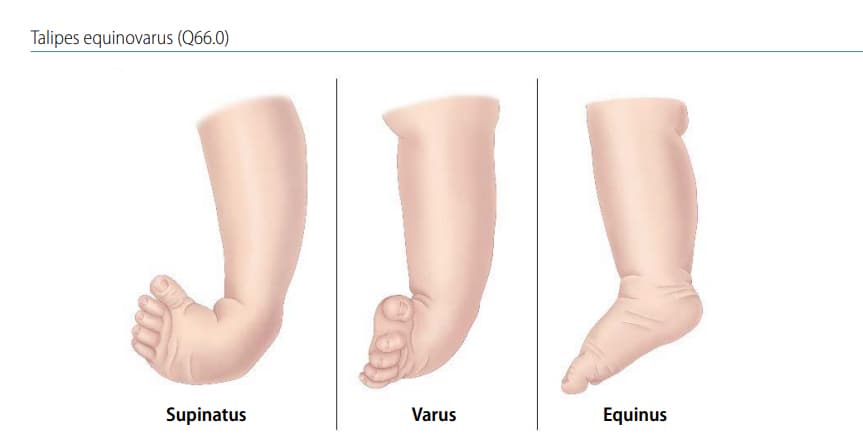



Chapter 4 9 Talipes Equinovarus Talipes Equinovarus Q66 0 Cdc




Talipes Club Foot Special Footwear And Orthotics



My Journey With Baby S Positional Clubfoot Part 1 Baby Gizmo



Ponseti Method Physiopedia



Club Foot Shoes Ponseti Denis Brown Dobs Bar Gm Medical Kenya




Clubfoot Repair Healthing Ca




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Narayana Health



Clubfoot What Is Clubfoot What Causes Clubfoot Who Gets Clubfoot What Are The Symptoms Of Clubfoot



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia




Congenital Clubfoot Genetic Disorders Types Of Clubfoot




Clubfoot Orthopaedia
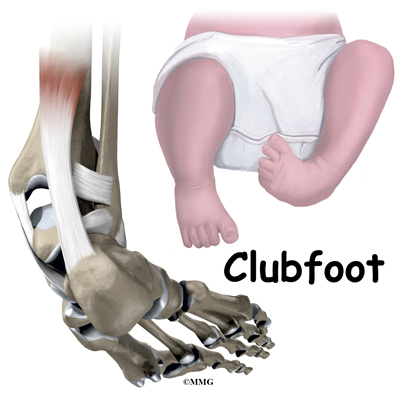



Clubfoot Eorthopod Com
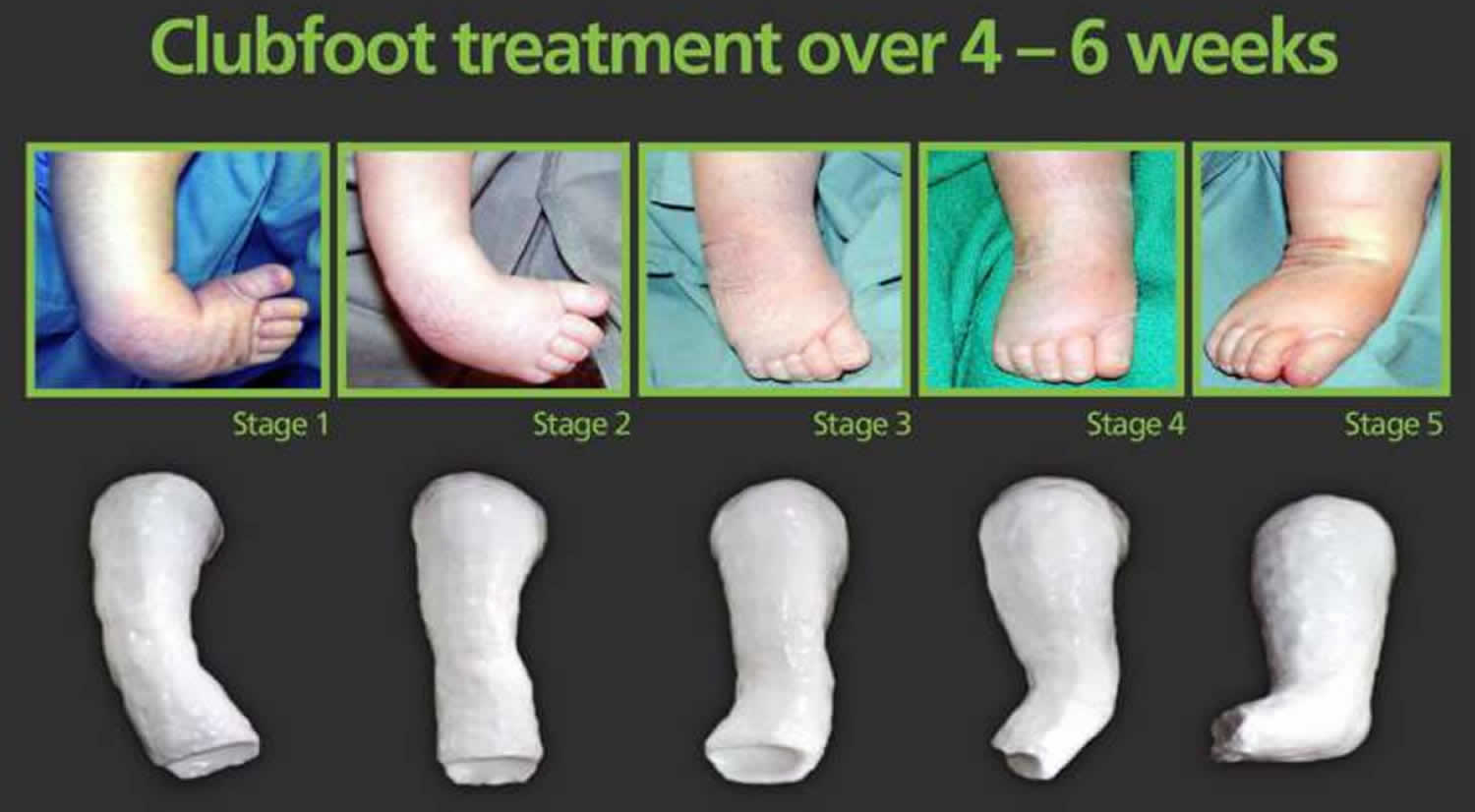



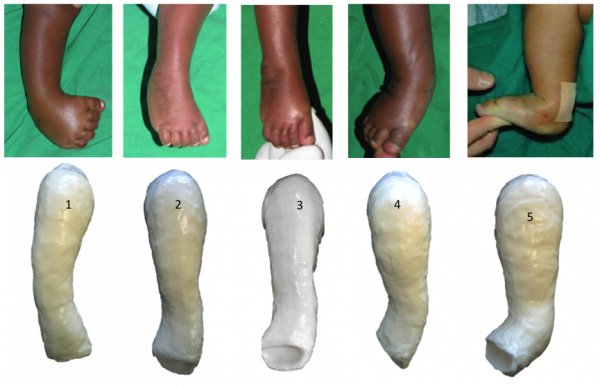
Ponseti Method For Clubfoot Treatment




Design And Development Of Orthosis For Clubfoot Deformity Springerlink
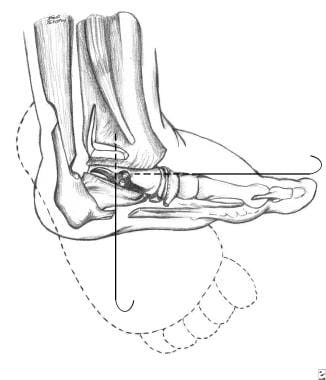



Clubfoot Talipes Treatment Management Approach Considerations Nonoperative Therapy Surgical Therapy




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Representative Case Of Severe Bilateral Clubfoot In A 3 Month Old Male Download Scientific Diagram



Ijerph Free Full Text A Community Audit Of 300 Drop Out Instances In Children Undergoing Ponseti Clubfoot Care In Bangladesh What Do The Parents Say Html




Clubfoot Wikipedia



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os




By Cassie Maier What Is Club Foot Club Foot Is When One Or Both Babies Feet Are Turned Inward And Downward And Cannot Be Put Into Normal Position Easily Ppt Download




Clinical Photographs Showing A The Club Feet Of A 1 5 Month Old Baby Download Scientific Diagram



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments




Clubfoot Wikipedia




Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot And Other Foot Abnormalities Pediatrics Merck Manuals Professional Edition



Club Foot Nhs




Challenging Clubfeet The Arthrogrypotic Clubfoot And The Complex Clubfoot Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics



Clubfoot Talipes Equinovarus Tev Youtube




Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot And Other Foot Abnormalities Pediatrics Merck Manuals Professional Edition




Current Concepts With The Ponseti Technique




To Parents Of Children Born With Clubfeet University Of Iowa Stead Family Children S Hospital
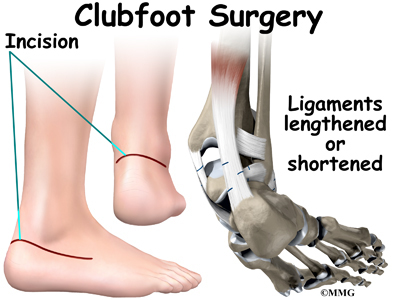



Clubfoot Eorthopod Com




Talipes Deformity Case Study Clubfoot Nursing Crib




Treatment Of Relapsed Residual And Neglected Clubfoot Adjunctive Surgery Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics



1




55 Talipes Ideas Club Foot Club Foot Baby Feet



1



Q Tbn And9gcsiqk2gm7zj3ssgnajpf1ujxpqe2efkyujjneftvigthk Bxfrn Usqp Cau




Clubb Foot




Clubfoot Eorthopod Com
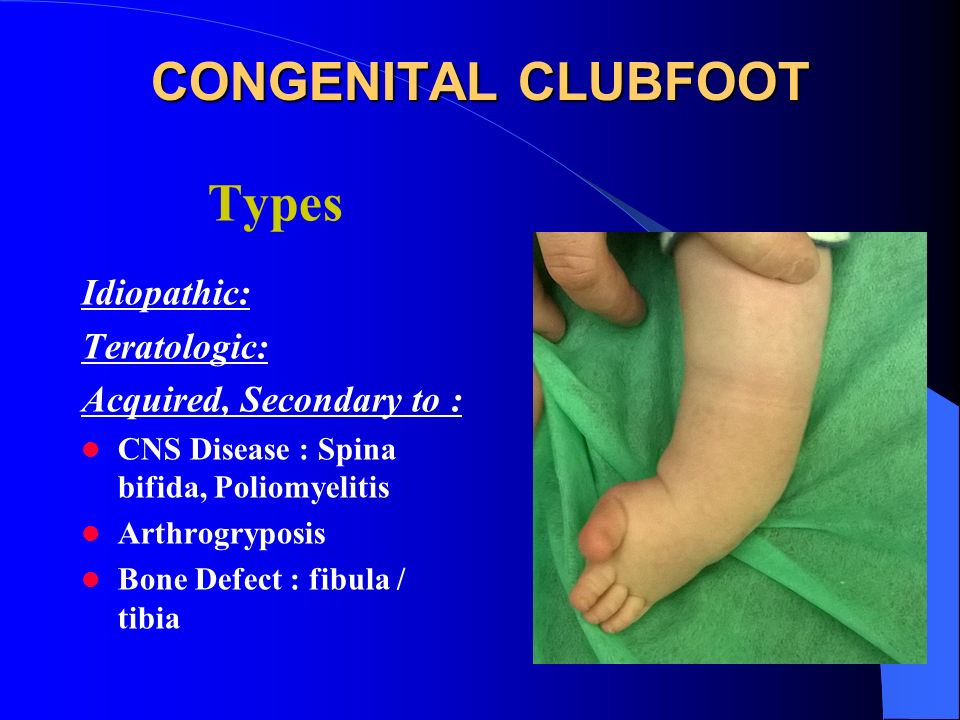



Congenital Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Ppt Video Online Download



Congenital Club Foot In Child Kerala Nurses Hub Youtube




Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Merck Manuals Consumer Version




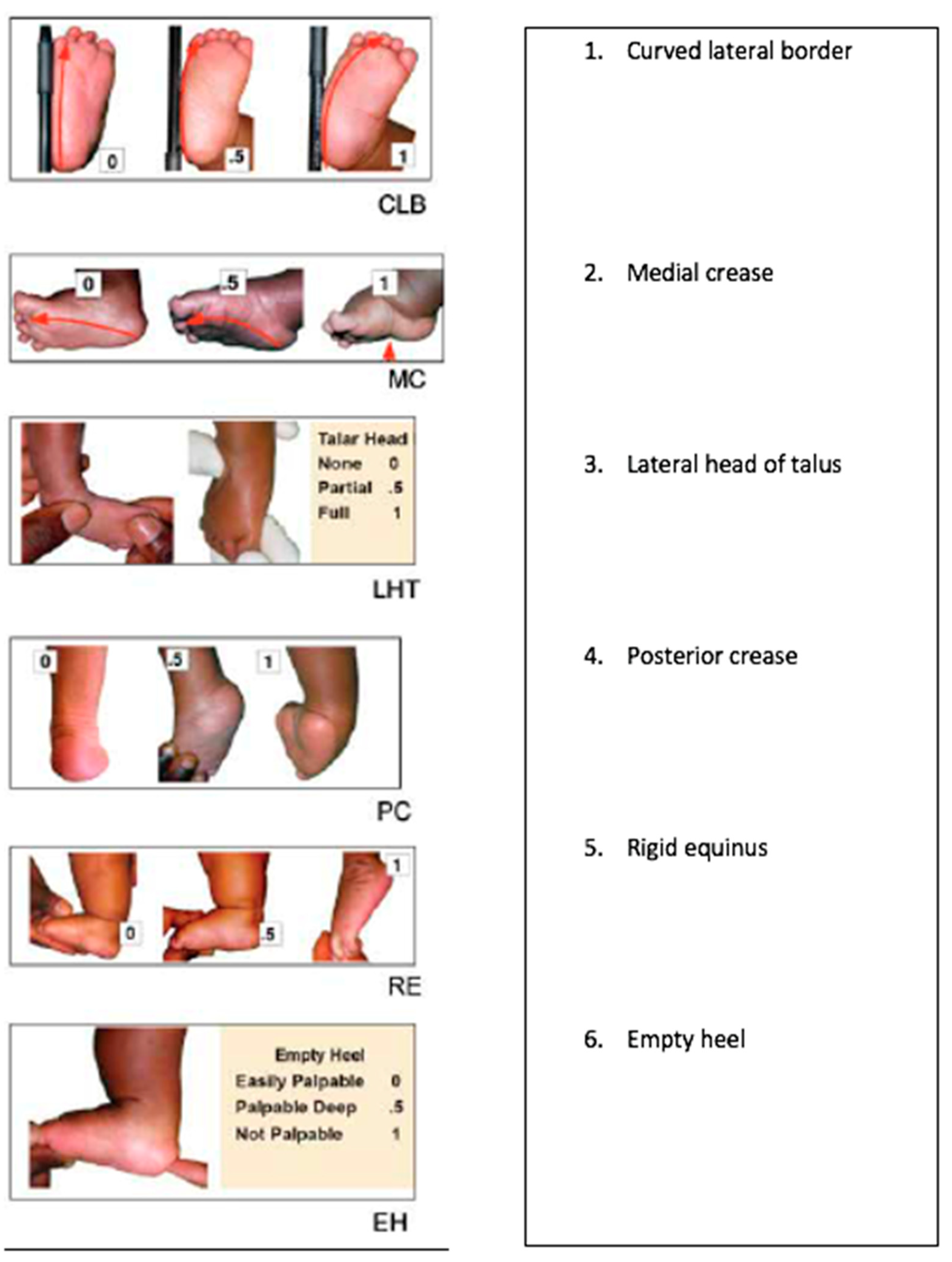
Dimeglio Score Evaluation A Bilateral Clubfoot B Varus 3 C Download Scientific Diagram




Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital



コメント
コメントを投稿